Node-RED on the Turck IM18-CCM50
This tutorial explains how to install and use Node-RED on the Turck IM18-CCM50. The IM18-CCM50 is a small industrial Linux computer, suitable for placing in control cabinets. More information about the IM18-CCM50 can be found on the Turck website.
Node-RED is a programming tool for wiring together hardware devices, APIs and online services in new and interesting ways. It provides a browser-based editor that makes it easy to wire together flows using the wide range of nodes in the palette that can be deployed to its runtime in a single-click.
Connect to the IM18-CCM50
By default the ethernet interfaces are set the DHCP. The default IP addresses when no DHCP server is active are 192.168.1.20 for ETH0 and 192.168.2.20 for ETH1. After powering up the device and connecting via ethernet it is possible to access the device via SSH. A client like PuTTY can be used. The user is sshu and the default password is P@ssw0rd12ssh! It is recommended to change this password after the first login.
Installing Node-RED
The Node-RED documentation tells us that first Node.js needs to be installed. In the FAQ the recommended and supported versions of Node.js can be found. I recommend to use the most recent supported LTS release of Node.js. Check the Node.js website for information about the current LTS release. At the time of writing Node.js V14 is recommended by Node-RED. Also the modbus package we will install later is not yet supported with Node.js V16.
The Node.js documentation explains that an installation package for Node.js is provided by NodeSource. Use the following commands to install Node.js on the IM18-CCM50:
sudo curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_14.x | sudo bash -
sudo apt install -y nodejs
To install Node-RED the npm command can be used. Use the following command to install Node-RED:
sudo npm install -g --unsafe-perm node-red
Node-RED can be started by executing the following command via SSH:
sudo node-red
Now Node-RED is available to access via a webbrowser at port 1880. For example: http://192.168.2.20:1880. You can use Ctrl-C or close the terminal window to stop Node-RED.
To start Node-RED on boot, a script needs to be added. The script is available on github. It can be installed with 1 command:
sudo wget -O /tmp/node-red https://gist.githubusercontent.com/SankariNL/afe080d53b90ffe19081e720b569a319/raw && sudo mv /tmp/node-red /etc/init.d && sudo chmod +x /etc/init.d/node-red && sudo update-rc.d node-red defaults
The file can also be manually added to the /etc/init.d folder via SCP for example. Then the chmod and update-rc.d commands need to be executed manually.
Reboot the IM18-CCM50 and access Node-RED via the webbrowser again.
Using the available scripts
When Node-RED is installed and running, it is possible to use the scripts that are delivered with the IM18-CCM50. These scripts are located in the /home/scripts directory as mentioned in chapter 7.3 of the manual. Scripts can be executed by Node-RED by using the default exec node. To execute the ambient_read.sh script input the following as the command: /home/scripts/ambient_read.sh.
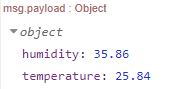
There is a flow available where the ambient_read.sh script is executed every 30 seconds (this can be changed after importing) and the result is added to the msg object. The flow looks like this:
When observing de debug output it shows the payload object with the humidity and temperature:
Installing additional Node-RED submodule for Modbus
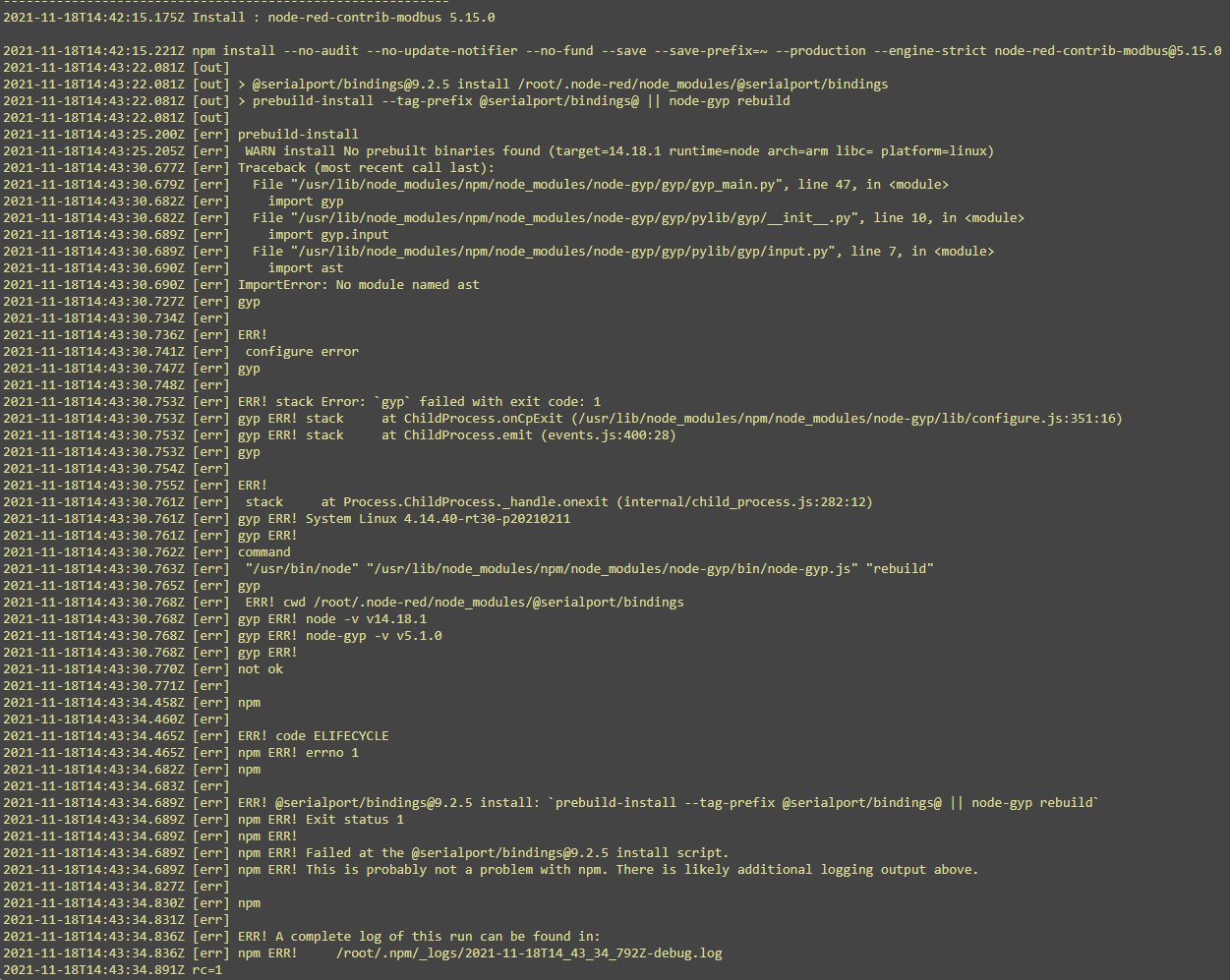
To use Modbus in Node-RED an additional package needs to be installed. There are several packages available, in this tutorial we will use the node-red-contrib-modbus package. Normally packages can be added by using the manage palette menu option. However, when trying this the following error shows up in the installation log:
This is because the SerialPort Node.js package could not be installed. The IM18-CCM50 uses a Texas instruments Sitara processor that is based on ARM v7. According to the documentation of SerialPort this is not a supported platform, but will probably work. To get it to work we need to compile the SerialPort package from scratch.
For this we need the build-essential package and python 2.7.
Use the following command to install the build-essential package:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt install build-essential
Install the python2.7 package because by default only the minimal python package is installed. SerialPort uses the ast package that is not included in the minimal python installation.
sudo apt install python2.7
Now compile and install the Node.js package with the following command:
sudo npm install -g serialport --unsafe-perm --build-from-source
Now it is possible to install the node-red-contrib-modbus package via the manage palette function in Node-RED. After installing the new modbus related nodes show up on the left side in Node-RED.
Using modbus in Node-RED
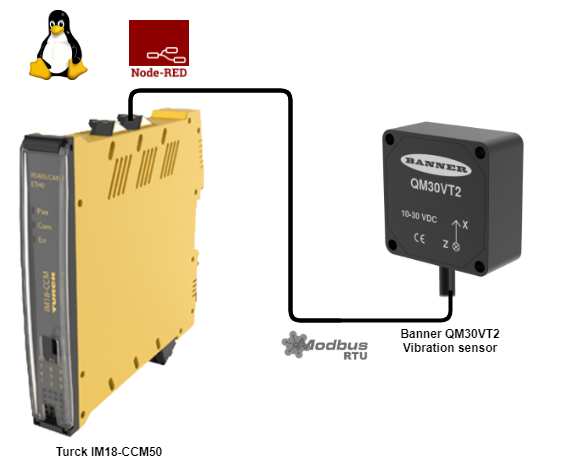
To use the modbus connection, first a modbus device needs to be connected. I’ve used the QM30VT2 vibration sensor from Banner Engineering that measures vibration and temperature. Attach 24V to pin 1 and 3, and attach pin 4(A) and 2(B) to pin 4(A) and 5(B) of the CAN port of the IM18-CCM50.
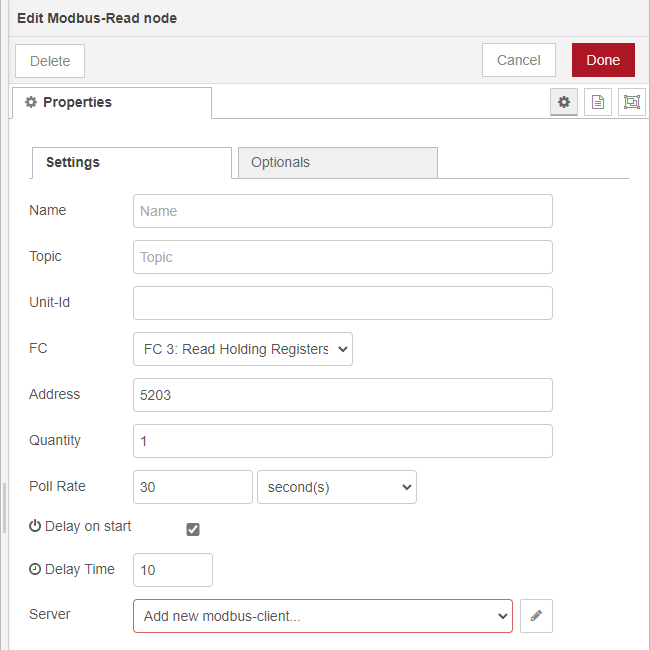
To use the modbus serial connection use the Modbus - Read node to read a register from a connected modbus device. Here fill in the following settings to access the temperature modbus register from the QM30VT2 sensor:
According to the manual the register alias adress is 45204. The 4 indicates that this is a holding register. So the FC is FC 3: Read Holding Registers. The address 5204 is offset by 1, so that’s why the address to look for is 5203. It’s possbile to read out multiple registers at once, but we only read 1 register. Since modbus is based on polling, a poll rate can be set.
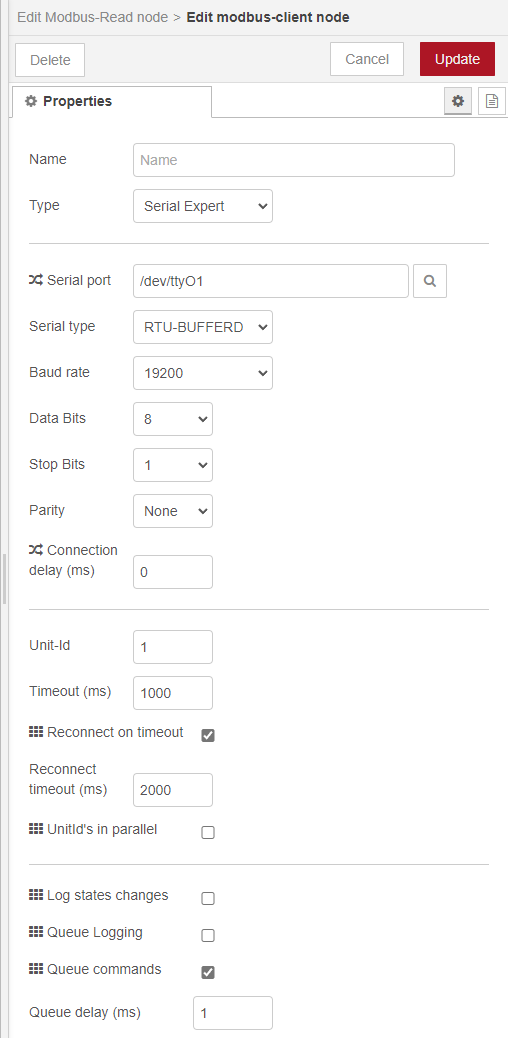
The last dropdown is Server. Here a modbus-client needs to be configured to be able to read modbus registers. Click the small pencil to add a new modbus-client config node.
Choose Serial Expert as the type. The serial port can be searched, or filled in manually. For the IM18-CCM50 this is always the /dev/ttyO1 device. The serial type should be RTU-BUFFERD. The modbus settings are 19200 baud-rate with 8 data bits and 1 stop bit, without parity. The Unit-Id is the default modbus address, used only if no other address is specified in a Modbus-read of write node.
There is a flow available where the modbus-read node is executed every 30 seconds (this can be changed after importing) and the result is added to the msg object. The flow looks like this:
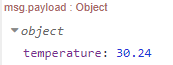
When observing de debug output it shows the payload object with the temperature:
In this tutorial we’ve seen multiple ways on how to measure temperature with the IM18-CCM50 together with Node-RED. In an upcoming tutorial I hope to show multiple ways on how to store and view the data we collected in this tutorial. If you have any more ideas, please let me know!